串口通信下
OpenMV串口调试扩展板
OpenMV串口调试扩展板将OpenMV的串口UART3,通过cp2104芯片连接到电脑,通过USB连接到串口调试扩展板,可以看到OpenMV的串口UART3上发送的数据。
https://singtown.com/product/49906
OpenMV和串口调试扩展板,通过2条USB线,都连接到电脑。
使用TTL-USB模块
如果没有OpenMV串口调试扩展板,也可以使用TTL-USB模块,他的作用和OpenMV串口调试扩展板一样。
首先我们要了解的是:各种单片机(包括Arduino, OpenMV, esp8266, stm32, 51)使用的串口都是TTL串口!不是rs485,不是rs232!
TTL串口的电压是3.3V或者5V,RS232的电压是+-15V,RS485的电压是5V,但是两根数据线是差分线,协议不一样,不能通用的。
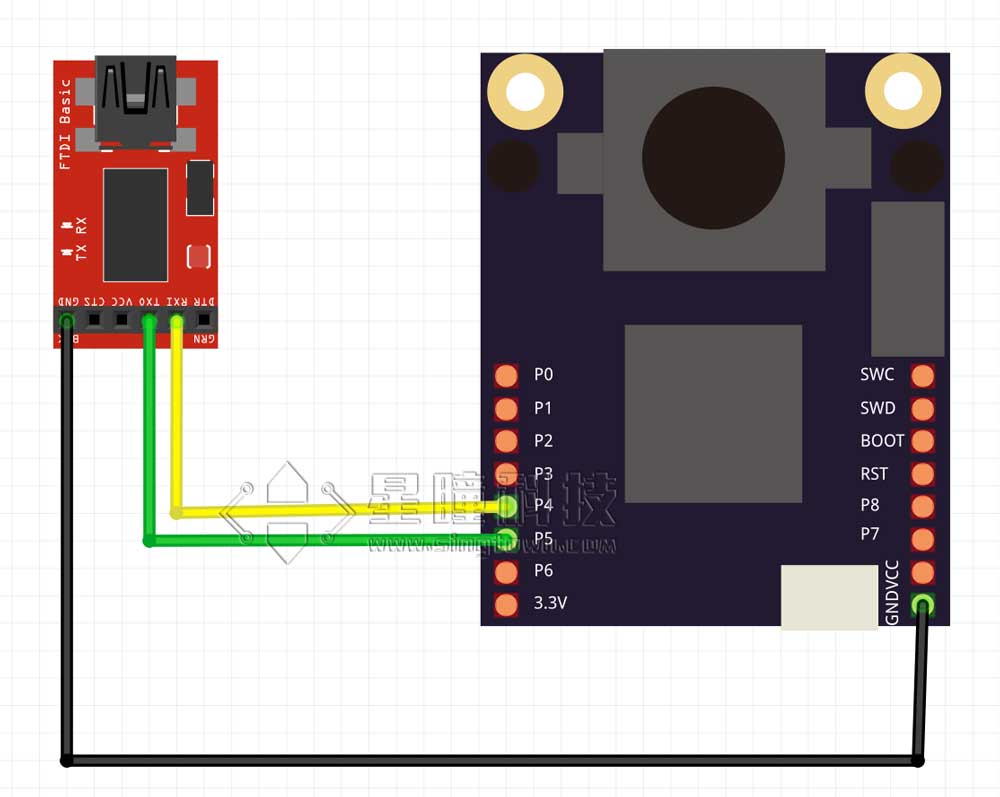
我们使用的模块是TTL转USB模块(推荐使用cp2104模块,稍微贵一点,但是质量好):

连接图(注意共地和RXTX交错连接):
| OpenMV | FTDI |
|---|---|
| P4(TX) | RX |
| P5(RX) | TX |
| GND | GND |
将TTL模块的USB端插入电脑,会出现一个串口。
星瞳串口助手
首先下载星瞳串口助手:
https://singtown.com/singtownserialport/
星瞳串口助手是一款,简洁易用,支持Windows,MacOS,Linux的开源的串口助手。
运行程序
注意,有些软件是可以选择HEX(16进制)或者ASC(ascii),要选择ASC,才能显示字符串。
OpenMV上运行uart.write("hello world!")的程序(见上节)。
在串口助手会显示Hello world!字符。
如果运行下面的程序:
import sensor, image, time
import json
from machine import UART
#from pyb import UART
# For color tracking to work really well you should ideally be in a very, very,
# very, controlled enviroment where the lighting is constant...
yellow_threshold = ( 46, 100, -68, 72, 58, 92)
# You may need to tweak the above settings for tracking green things...
# Select an area in the Framebuffer to copy the color settings.
sensor.reset() # Initialize the camera sensor.
sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) # use RGB565.
sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QQVGA) # use QQVGA for speed.
sensor.skip_frames(10) # Let new settings take affect.
sensor.set_auto_whitebal(False) # turn this off.
clock = time.clock() # Tracks FPS.
# OpenMV4 H7 Plus, OpenMV4 H7, OpenMV3 M7, OpenMV2 M4 的UART(3)是P4-TX P5-RX
uart = UART(3, 115200) #OpenMV RT 注释掉这一行,用下一行UART(1)
#uart = UART(1, 115200) #OpenMV RT 用UART(1)这行,注释掉上一行UART(3)
# OpenMV RT 只有串口UART(1),对应P4-TX P5-RX; OpenMV4 H7 Plus, OpenMV4 H7, OpenMV3 M7 的UART(1)是P0-RX P1-TX
while(True):
clock.tick() # Track elapsed milliseconds between snapshots().
img = sensor.snapshot() # Take a picture and return the image.
blobs = img.find_blobs([yellow_threshold])
if blobs:
#print('sum : %d'% len(blobs))
data=[]
for b in blobs:
# Draw a rect around the blob.
img.draw_rectangle(b.rect()) # rect
img.draw_cross(b.cx(), b.cy()) # cx, cy
data.append((b.cx(),b.cy()))
#{(1,22),(-3,33),(22222,0),(9999,12),(0,0)}
data_out = json.dumps(set(data))
uart.write(data_out +'\n')
print('you send:',data_out)
else:
print("not found!")
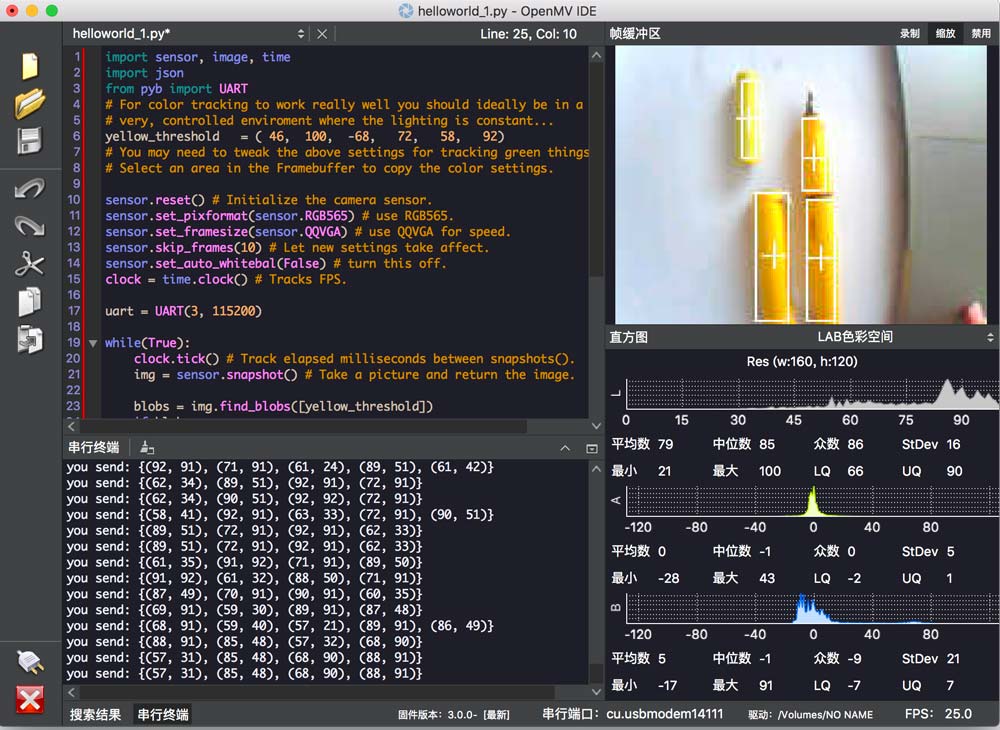
会将所有的色块的中心坐标发出去。
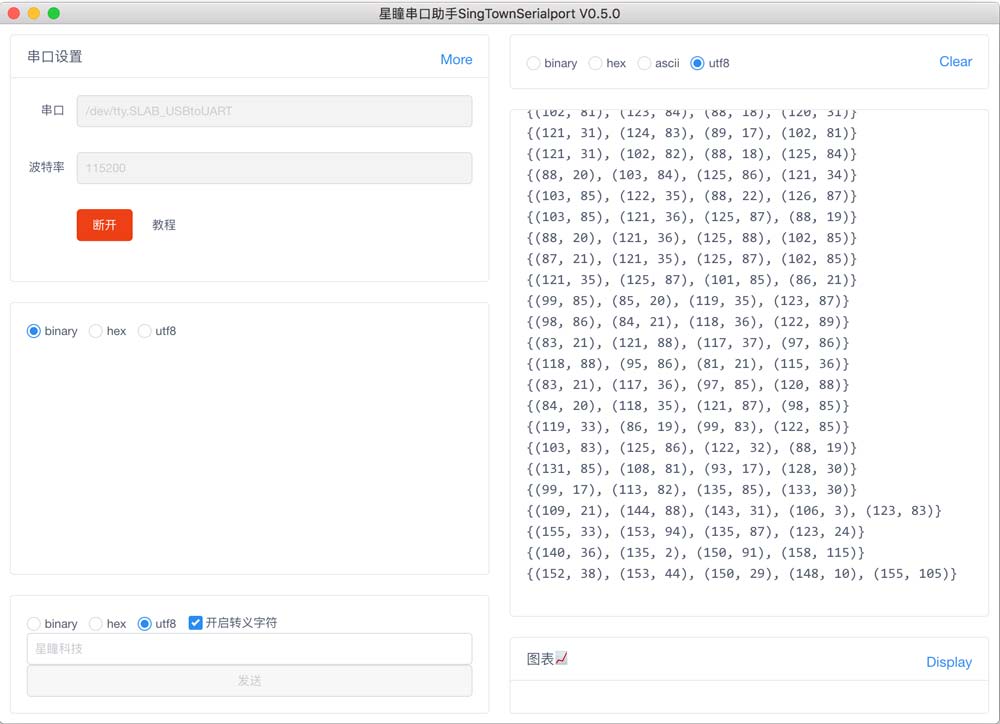
星瞳串口助手会显示接收到的数据:
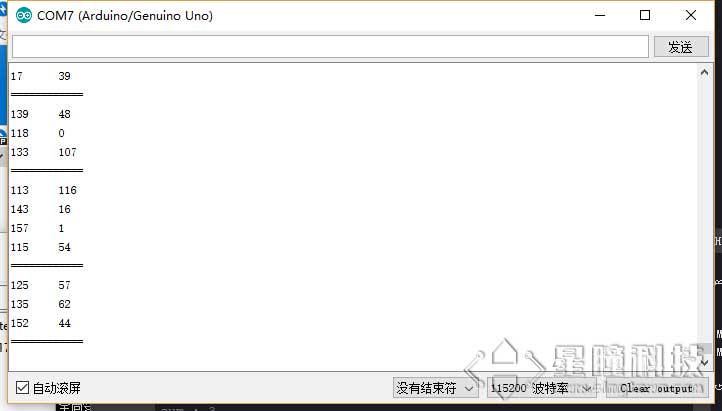
Arduino解析程序
因为Arduino Uno只有一个串口,一个用来接受,就没办法发送给电脑显示了。所以我们使用软件模拟串口,来进行串口转发程序。
| OpenMV | Arduino |
|---|---|
| P4(TX) | 10(RX) |
| P5(RX) | 11(TX) |
| GND | GND |
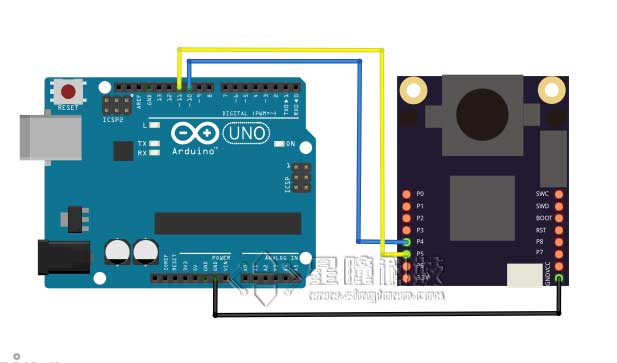
转发逻辑是这样的:OpenMV的数据发送给Arduino Uno的软串口,Arduino的串口连接到电脑并显示结果的。
所以,在ArduinoMega的逻辑就是:读softSerial的数据(json),然后解析成数组,发送给Serial(电脑)。
代码
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial softSerial(10, 11); // RX, TX
typedef struct
{
int data[50][2] = {{0,0}};
int len = 0;
}List;
List list;
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
softSerial.begin(115200);
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop() {
if(softSerial.available())
{
getList();
for (int i=0; i<list.len; i++)
{
Serial.print(list.data[i][0]);
Serial.print('\t');
Serial.println(list.data[i][1]);
}
Serial.println("============");
clearList();
}
}
String detectString()
{
while(softSerial.read() != '{');
return(softSerial.readStringUntil('}'));
}
void clearList()
{
memset(list.data, sizeof(list.data),0);
list.len = 0;
}
void getList()
{
String s = detectString();
String numStr = "";
for(int i = 0; i<s.length(); i++)
{
if(s[i]=='('){
numStr = "";
}
else if(s[i] == ','){
list.data[list.len][0] = numStr.toInt();
numStr = "";
}
else if(s[i]==')'){
list.data[list.len][1] = numStr.toInt();
numStr = "";
list.len++;
}
else{
numStr += s[i];
}
}
}