pyb各种外设
概览
作为一个单片机,控制IO口,IIC,SPI,CAN,PWM。定时器当然都是可以的。
而且,使用python语言,可以非常简单的调用它们,而不用考虑寄存器。
| Tables | OpenMV2 M4 | OpenMV3 M7 | OpenMV4 H7 | OpenMV4 H7 Plus | OpenMV RT1062 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin | 9 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 14 |
| ADC | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| DAC | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| SPI | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| I2C | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| UART | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Servo | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 |
| CAN bus | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
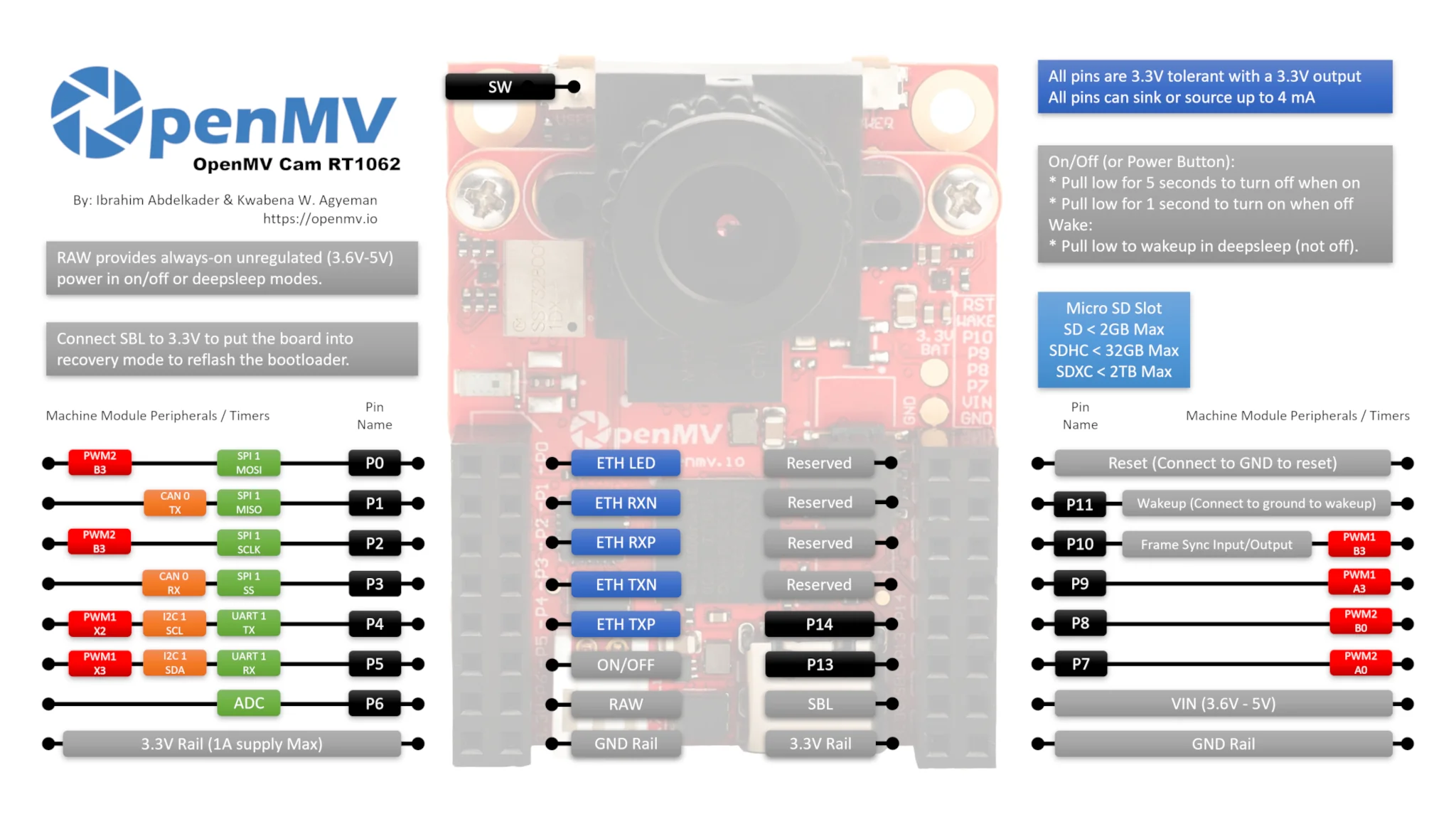
| 电源按键 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 自定义按键 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 引脚耐受 | 5V | 5V | 5V | 5V | 3.3V |
| 引脚电平 | 3.3V | 3.3V | 3.3V | 3.3V | 3.3V |
| IC | STM32F427 | STM32F765 | STM32H743 | STM32H743 | IMXRT1062 |
| RAM | 256KB | 512KB | 1MB | 32MB + 1MB | 32MB + 1MB |
| Flash | 1MB | 2MB | 2MB | 32MB + 2MB | 16MB |
| 频率 | 180MHz | 216MHZ | 480MHZ | 480MHZ | 600MHZ |
| 标配感光元件 | OV7725(30W像素) | OV7725(30W像素) | OV7725(30W像素) | OV5640(500W像素) | OV5640(500W像素) |
注意:因为MicroPython可以在很多平台上运行。最开始在pyb模块,pyboard,是基于STM32的,但是后来又加入了esp8266和esp32,以及nrf系列,他们的架构和STM32不同。所以官方统一制定了machine模块,所以通用性更高一些,最终pyb会被淘汰。
OpenMV4 H7 Plus / OpenMV4 H7 / OpenMV3,主控为STM32,一般用pyb模块。
2024年最新款的OpenMV RT1062,主控为IMXRT1062,只支持machine模块,不支持pyb模块。请使用对应的machine代码哦~
常用的函数
pyb.delay(50) # 延时 50 毫秒
pyb.millis() # 获取从启动开始计时的毫秒数
LED
from pyb import LED
led = LED(1) # 红led
led.toggle()
led.on()#亮
led.off()#灭
LED(1) -> 红LED
LED(2) -> 绿LED
LED(3) -> 蓝LED
LED(4) -> 红外LED,两个
在 OpenMV RT 上不能用pyb模块,只能使用以下machine模块:
from machine import LED
import time
red_led = LED("LED_RED")
green_led = LED("LED_GREEN")
blue_led = LED("LED_BLUE")
blue_led.off()
green_led.off()
red_led.off()
while(1):
green_led.toggle()
red_led.on()
time.sleep_ms(250)
red_led.off()
time.sleep_ms(250)
IO
from pyb import Pin
p_out = Pin('P7', Pin.OUT_PP)#设置p_out为输出引脚
p_out.high()#设置p_out引脚为高
p_out.low()#设置p_out引脚为低
p_in = Pin('P7', Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)#设置p_in为输入引脚,并开启上拉电阻
value = p_in.value() # get value, 0 or 1#读入p_in引脚的值
在 OpenMV RT 上不能用pyb模块,只能使用以下machine模块:
from machine import Pin
p_out = Pin("P7", Pin.OUT)#设置p_out为输出引脚
p_out.high()#设置p_out引脚为高
p_out.low()#设置p_out引脚为低
p_in = Pin("P8", Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)#设置p_in为输入引脚,并开启上拉电阻
value = p_in.value() # get value, 0 or 1#读入p_in引脚的值
Servo
视频教程34 - OpenMV控制三个舵机:https://singtown.com/learn/50541/
from pyb import Servo
s1 = Servo(1) # servo on position 1 (P7)
s1.angle(45) # move to 45 degrees
s1.angle(-60, 1500) # move to -60 degrees in 1500ms
s1.speed(50) # for continuous rotation servos
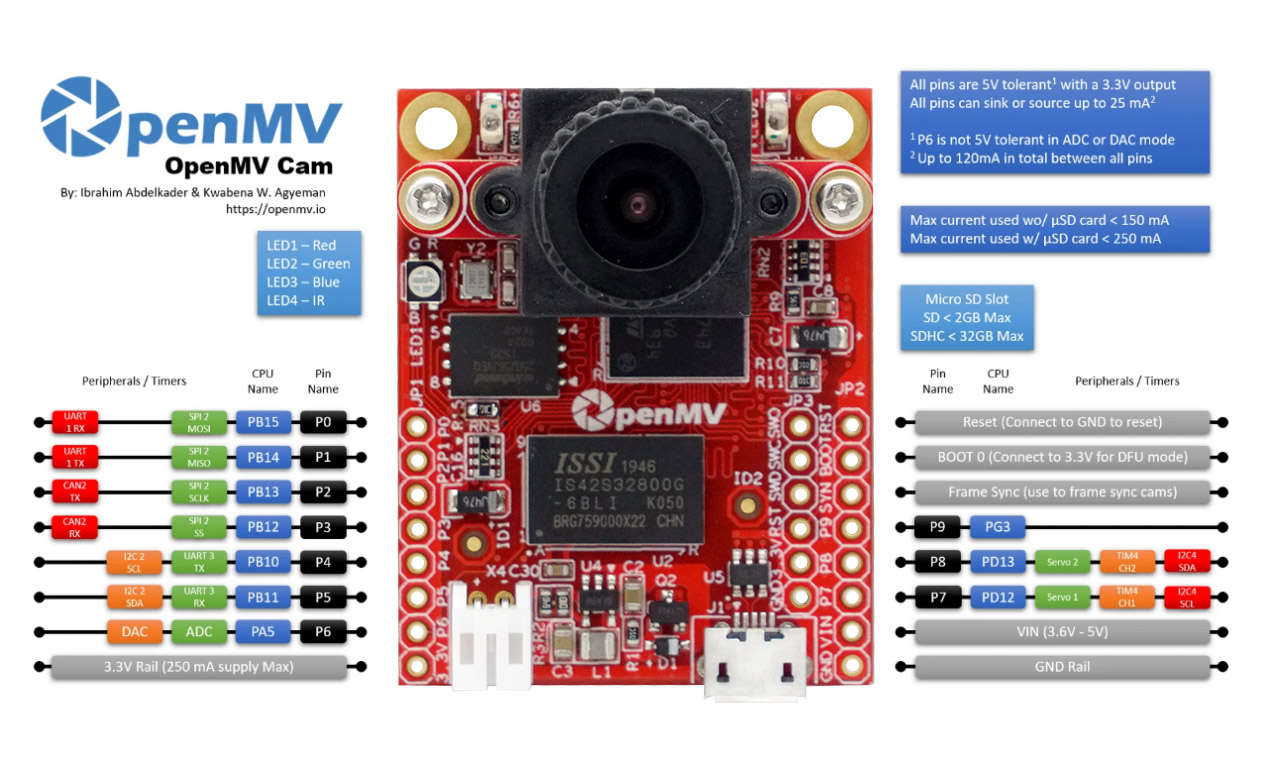
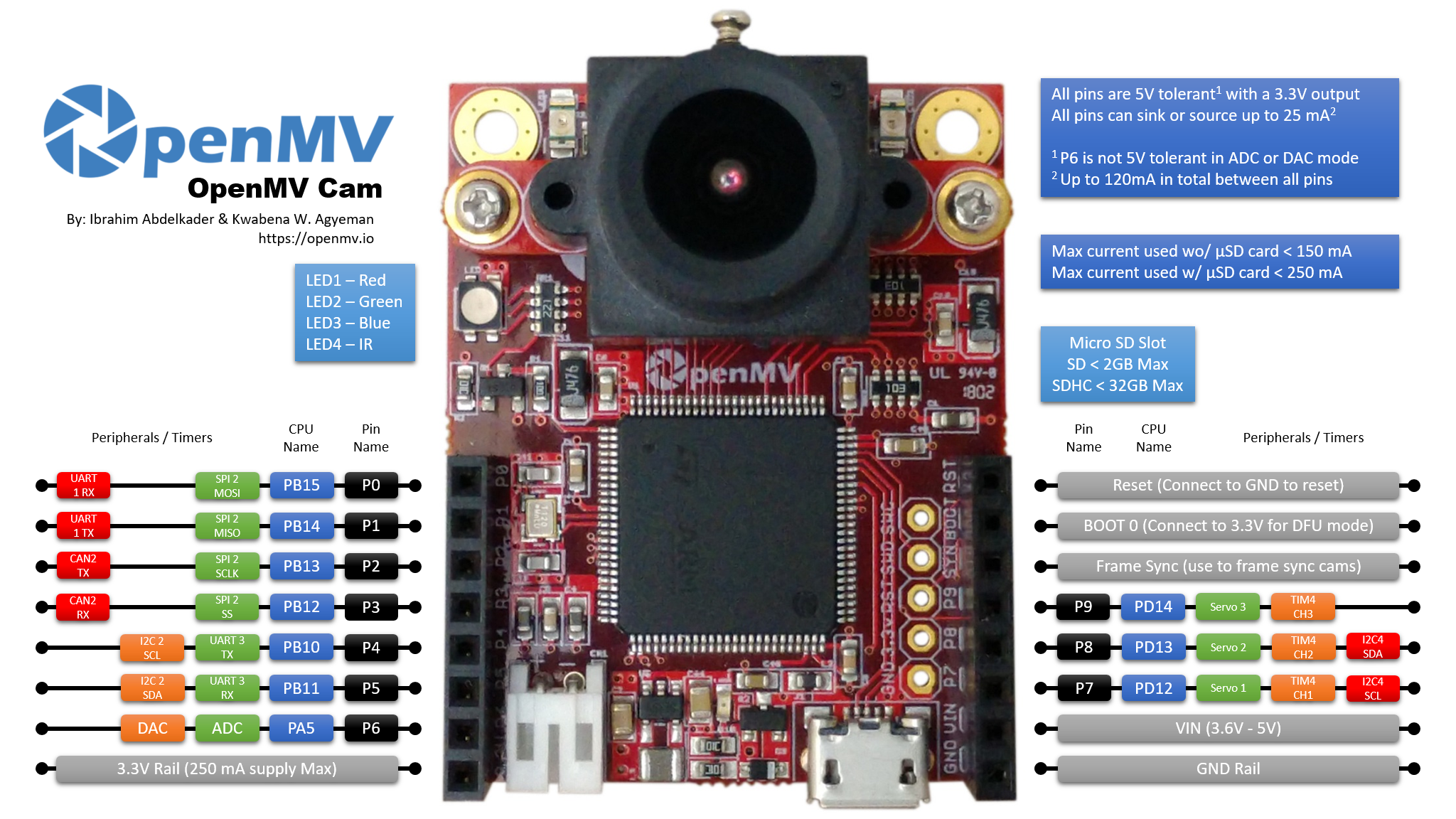
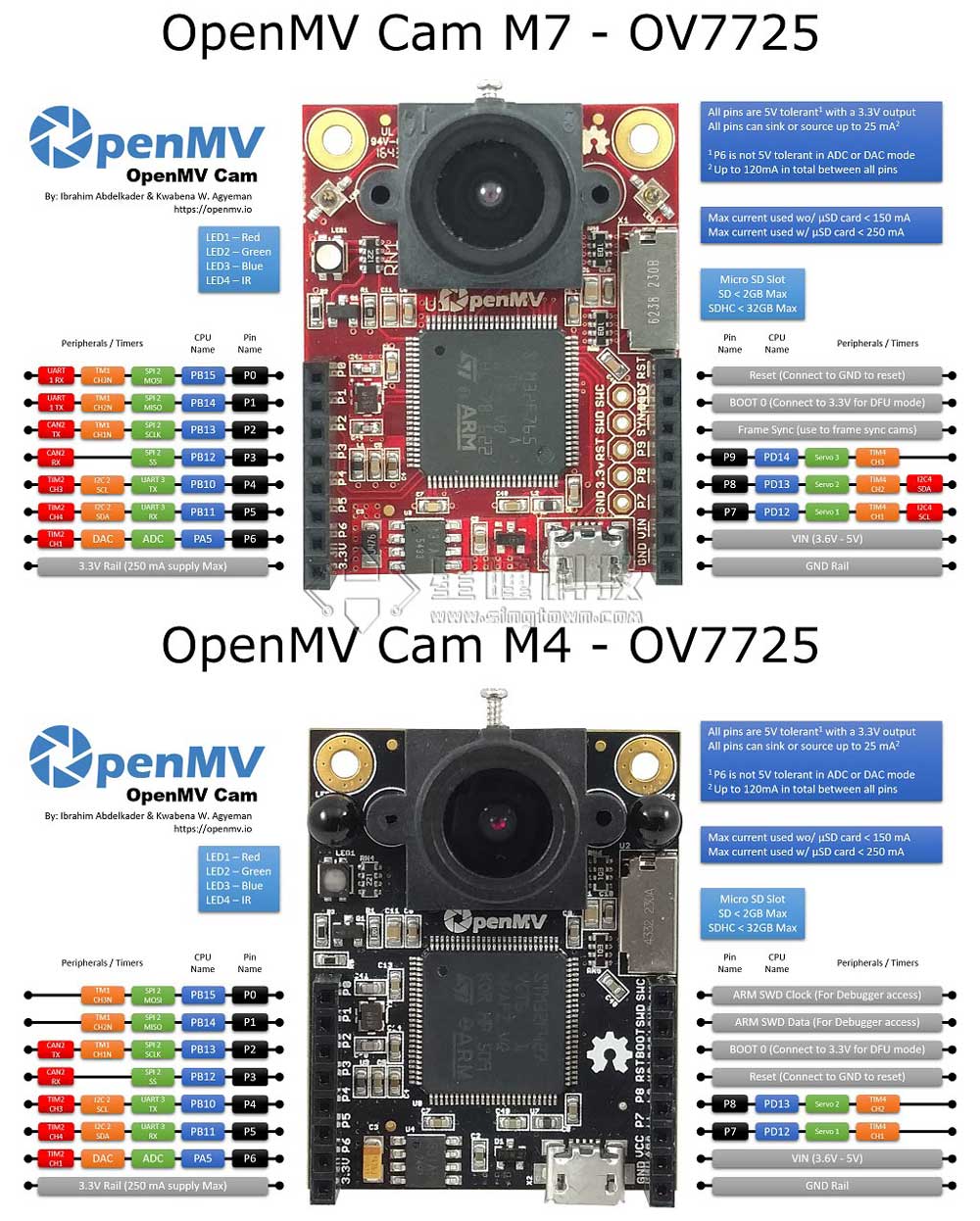
- Servo(1) -> P7 (PD12)
- Servo(2) -> P8 (PD13)
OpenMV3 M7 / OpenMV4 H7上增加:
- Servo(3) -> P9 (PD14)
注意:OpenMV4 H7 Plus P9不能使用PWM
OpenMV RT1062 有P7 P8 P9 P10 四个PWM引脚。 在 OpenMV RT 上不能用pyb模块,只能使用以下machine模块:
# 舵机控制例子
#
# 这个例子展示了如何使用OpenMV来控制舵机
#
# 伺服系统需要 50 Hz PWM,脉冲宽度为 1000us 至 2000us。
import time
from machine import PWM
# P7 和 P8 可以共享相同的 PWM module,它们需要具有相同的频率。
p7 = PWM("P7", freq=50, duty_ns=(2000 * 1000))
p8 = PWM("P8", freq=50, duty_ns=(2000 * 1000))
# P9 和 P10 可以共享相同的 PWM module,它们需要具有相同的频率。
p9 = PWM("P9", freq=50, duty_ns=(2000 * 1000))
p10 = PWM("P10", freq=50, duty_ns=(2000 * 1000))
while True:
for i in range(1000, 2000, 100):
p7.duty_ns(i * 1000)
p8.duty_ns(i * 1000)
p9.duty_ns(i * 1000)
p10.duty_ns(i * 1000)
time.sleep_ms(1000)
for i in range(2000, 1000, -100):
p7.duty_ns(i * 1000)
p8.duty_ns(i * 1000)
p9.duty_ns(i * 1000)
p10.duty_ns(i * 1000)
time.sleep_ms(1000)
IO中断
from pyb import Pin, ExtInt
callback = lambda e: print("intr")
ext = ExtInt(Pin('P7'), ExtInt.IRQ_RISING, Pin.PULL_NONE, callback)
在 OpenMV RT 上不能用pyb模块,只能使用以下machine模块:
from machine import Pin
import time
pin0 = Pin("P0", Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
callback = lambda e: print("intr")
pin0.irq(callback, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
while True:
time.sleep(1)
定时器
from pyb import Timer
tim = Timer(4, freq=1000)
tim.counter() # get counter value
tim.freq(0.5) # 0.5 Hz
tim.callback(lambda t: pyb.LED(1).toggle())
Timer 1 Channel 3 Negative -> P0
Timer 1 Channel 2 Negative -> P1
Timer 1 Channel 1 Negative -> P2
Timer 2 Channel 3 Positive -> P4
Timer 2 Channel 4 Positive -> P5
Timer 2 Channel 1 Positive -> P6
Timer 4 Channel 1 Negative -> P7
Timer 4 Channel 2 Negative -> P8
OpenMV M7上增加:
Timer 4 Channel 3 Positive -> P9
在 OpenMV RT 上不能用pyb模块,只能使用以下machine模块:
from machine import LED
from machine import Timer
blue_led = LED("LED_BLUE")
# 当被调用时,我们将返回timer对象
# 注意:在回调中不允许分配内存的函数
def tick(timer):
blue_led.toggle()
# machine模块目前仅支持-1虚拟定时器。
tim = Timer(-1, freq=1, callback=tick) # 创建一个定时器对象—以1Hz触发
PWM
from pyb import Pin, Timer
p = Pin('P7') # P7 has TIM4, CH1
tim = Timer(4, freq=1000)
ch = tim.channel(1, Timer.PWM, pin=p)
ch.pulse_width_percent(50)
在 OpenMV RT 上不能用pyb模块,只能使用以下machine模块:
from machine import PWM
import time
p7 = PWM("P7", freq=100, duty_u16=32768)
while True:
for i in range(0, 65536, 256):
p7.duty_u16(65535 - i)
time.sleep_ms(10)
p7.duty_u16(32768)
ADC
from pyb import Pin, ADC
adc = ADC('P6')
adc.read() # read value, 0-4095
在 OpenMV RT 上不能用pyb模块,只能使用以下machine模块:
from machine import ADC
adc = ADC('P6')
adc.read_u16()
DAC
from pyb import Pin, DAC
dac = DAC('P6')
dac.write(120) # output between 0 and 255
UART
from pyb import UART
uart = UART(3, 9600)
uart.write('hello')
uart.read(5) # read up to 5 bytes
UART 3 RX -> P5 (PB11)
UART 3 TX -> P4 (PB10)
OpenMV3 M7 / OpenMV4 H7/ OpenMV4 H7 Plus上增加:
UART 1 RX -> P0 (PB15)
UART 1 TX -> P1 (PB14)
在 OpenMV RT 上不能用pyb模块,只能使用以下machine模块:
from machine import UART
uart = UART(1, 9600)
uart.write('hello')
uart.read(5) # read up to 5 bytes
OpenMV RT1062只有串口1,对应 P4 P5 引脚。
UART 1 RX -> P5 (PB11)
UART 1 TX -> P4 (PB10)
SPI
from pyb import SPI
spi = SPI(2, SPI.MASTER, baudrate=200000, polarity=1, phase=0)
spi.send(b'hello')
spi.recv(5) # receive 5 bytes on the bus
spi.send_recv(b'hello') # send a receive 5 bytes
在 OpenMV RT 上不能用pyb模块,只能使用以下machine模块:
from machine import SPI
spi = SPI(1, baudrate=int(1000000000 / 66), polarity=0, phase=0)
spi.write(b'hello')
spi.read(5) # receive 5 bytes on the bus
txdata = b"12345678"
rxdata = bytearray(len(txdata))
spi.write_readinto(txdata, rxdata) # Simultaneously write and read bytes.
I2C
from machine import I2C, Pin
i2c = I2C(sda=Pin('P5'),scl=Pin('P4'))
i2c.scan()
i2c.writeto(0x42, b'123') # write 3 bytes to slave with 7-bit address 42
i2c.readfrom(0x42, 4) # read 4 bytes from slave with 7-bit address 42
i2c.readfrom_mem(0x42, 8, 3) # read 3 bytes from memory of slave 42,
# starting at memory-address 8 in the slave
i2c.writeto_mem(0x42, 2, b'\x10') # write 1 byte to memory of slave 42
# starting at address 2 in the slave
I2C 2 SCL (Serial Clock) -> P4 (PB10)
I2C 2 SDA (Serial Data) -> P5 (PB11)
OpenMV3 M7 / OpenMV4 H7 / OpenMV4 H7 Plus上增加:
I2C 4 SCL (Serial Clock) -> P7 (PD13)
I2C 4 SDA (Serial Data) -> P8 (PD12)
machine库是软件模拟的I2C协议,所以使用任何引脚都可以,但是还是推荐使用上面所说的引脚。
在 OpenMV RT 上可以这样调用:
from machine import I2C, Pin
i2c = I2C(1)
i2c.scan()
i2c.writeto(0x42, b'123') # write 3 bytes to slave with 7-bit address 42
i2c.readfrom(0x42, 4) # read 4 bytes from slave with 7-bit address 42
i2c.readfrom_mem(0x42, 8, 3) # read 3 bytes from memory of slave 42,
# starting at memory-address 8 in the slave
i2c.writeto_mem(0x42, 2, b'\x10') # write 1 byte to memory of slave 42
# starting at address 2 in the slave
Switch Pin 自定义按键SW
# OpenMV Cam 上的用户开关可通过“SW”引脚读取。
# 该引脚通过 RC 电路在硬件中进行去抖。
# 因此,您只需读取引脚状态即可了解开关是否被按下。
import machine
sw = machine.Pin("SW", machine.Pin.IN)
r = machine.LED("LED_RED")
while True:
r.value(not sw.value())
print(sw.value())
仅OpenMV RT具有SW自定义按键,OpenMV4 H7 / OpenMV4 H7 Plus / OpenMV3 M7 没有自定义按键。